Knee pain can significantly affect your quality of life, making even simple tasks challenging. Fortunately, various options exist for those struggling with joint issues, including different knee surgeries. One of the most effective solutions is knee replacement surgery, which helps restore mobility and reduce pain. In this blog, we will explore the types of knee replacement surgery, highlighting insights from renowned orthopedic surgeon Dr. Madan Mohan Reddy. Understanding the available options, such as total and partial knee Endoscopic Spine Surgery Cost in Chennai replacements, as well as other joint replacement surgery types, will help you choose the best path for your recovery.
What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
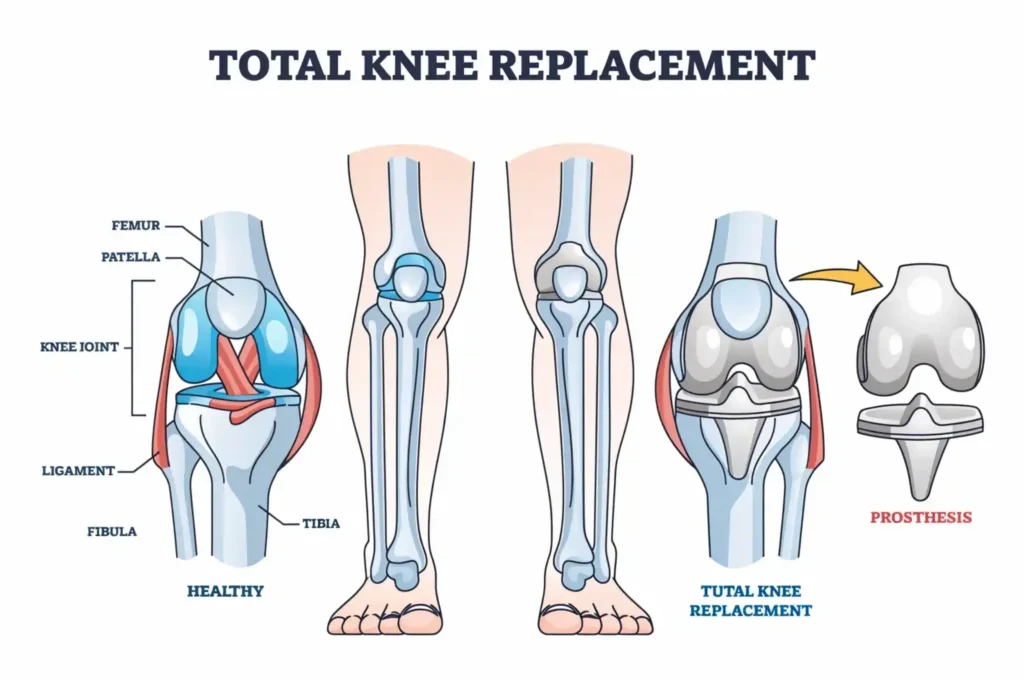
Knee replacement surgery is a medical procedure that involves replacing damaged or worn parts of the knee joint with artificial components. This surgery is typically recommended for patients suffering from severe arthritis or knee injuries that significantly impair movement and cause chronic pain. Among the different knee surgeries, the best type of total knee replacement is designed to restore normal function and alleviate discomfort. During this procedure, the damaged cartilage and bone are removed, and a prosthetic joint is inserted, allowing for smoother movement. It’s essential to consult with a qualified orthopedic surgeon to determine the most suitable option for your specific condition.
6 Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
There are several common types of knee replacement surgery available today. Each type serves a unique purpose based on the patient’s condition. Here are the primary types of knee replacement surgeries:
- Total Knee Replacement: This involves replacing the entire knee joint.
- Partial Knee Replacement: This surgery replaces only the damaged part of the knee.
- Revision Knee Replacement: This is performed when a previous knee replacement fails.
- Bilateral Knee Replacement: This procedure addresses both knees in one surgery.
- Patellofemoral Replacement: This surgery focuses on the kneecap and the area around it.
- Robot-Assisted Knee Replacement: A more advanced technique using robotic assistance for precision.
Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement is one of the most common procedures performed on patients with severe knee damage. It involves the complete replacement of the knee joint with a prosthetic device. This procedure is considered the best type of total knee replacement for those suffering from debilitating pain and limited mobility. The surgery typically lasts between 1.5 to 2 hours and requires a hospital stay for recovery. Surgeons, like Dr. Madan Mohan Reddy, emphasize that patients can expect significant pain relief and improved function after the procedure.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia is administered.
- Incision: A large incision is made on the knee.
- Joint Replacement: The damaged joint surfaces are removed and replaced with metal and plastic components.
- Closing Up: The incision is closed with stitches or staples.
Risks
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Prosthesis failure
- Nerve damage
Benefits
- Reduced pain
- Improved mobility
- Enhanced quality of life
- Long-lasting results
Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement is another effective option for patients with damage confined to a specific area of the knee. This surgery focuses on only replacing the damaged compartment of the knee, leaving the healthy parts intact. This type of surgery is gaining popularity among patients seeking less invasive options and quicker recovery times. It falls under the broader category of types of knee replacement surgery.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: Patients receive either general or local anesthesia.
- Incision: A smaller incision is made compared to total knee replacement.
- Joint Replacement: Only the damaged compartment is replaced.
- Closing Up: The incision is stitched or stapled.
Risks
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Reoperation needed if the other compartments deteriorate
Benefits
- Quicker recovery time
- Less pain and swelling
- Preserves healthy bone and tissue
- Smaller incision means less scarring
Revision Knee Replacement
Revision knee replacement is performed when a previous knee replacement fails or wears out. This type of surgery aims to replace the original prosthetic joint with a new one and may involve correcting any underlying issues contributing to the failure. It is important to understand that revision surgeries can be more complex, making them a significant option among the types of knee replacement surgery.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is used.
- Incision: The previous incision is reopened.
- Removal of Prosthesis: The old prosthesis is carefully removed.
- Insertion of New Prosthesis: A new joint is placed, sometimes requiring additional bone support.
- Closing Up: The incision is closed as per standard practices.
Risks
- Infection
- Instability of the new joint
- Fracture of the bone
- Longer rehabilitation period
Benefits
- Relief from pain
- Improved functionality
- Addressing issues from previous surgeries
- Enhanced quality of life
Bilateral Knee Replacement
Bilateral knee replacement involves replacing both knees simultaneously. This option is often considered for patients with severe osteoarthritis affecting both knees, allowing for a comprehensive approach to recovery. Although this surgery is a significant undertaking, it offers benefits to those needing intervention on both knees, emphasizing the types of knee replacement surgery.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: Typically, general anesthesia is used.
- Incision: Incisions are made on both knees.
- Joint Replacement: Both knees are treated in one session.
- Closing Up: The incisions are stitched or stapled.
Risks
- Longer hospital stay
- Higher risk of complications
- Increased recovery time
Benefits
- Simultaneous recovery from both knees
- Reduced total time spent in rehabilitation
- One surgical experience instead of two
- Cost-effective in some cases
Patellofemoral Replacement
Patellofemoral replacement is a specialized type of knee surgery focusing on the kneecap area. This procedure is ideal for patients with arthritis localized to the front of the knee and can provide significant pain relief and improved mobility without performing a total knee replacement. As one of the types of knee replacement surgery, it is gaining recognition among those with specific joint issues.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: Patients receive general anesthesia.
- Incision: A smaller incision is made around the kneecap.
- Replacement: The damaged cartilage and bone are replaced with a prosthetic.
- Closing Up: The incision is stitched or stapled.
Risks
- Infection
- Misalignment of the kneecap
- Limited improvement in knee function
Benefits
- Preserves healthy joint structures
- Faster recovery compared to total knee replacement
- Less postoperative pain
- Reduced scarring due to smaller incisions
Robot-Assisted Knee Replacement
Robot-assisted knee replacement uses advanced robotic technology to aid surgeons in performing knee replacement surgeries with enhanced precision. This innovative technique can lead to better alignment of the prosthetic joint and potentially shorter recovery times. As part of the types of knee replacement surgery, this option is becoming increasingly popular due to its benefits.
Procedure
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is usually administered.
- Preparation: The robot is set up and calibrated for the patient.
- Surgery: The surgeon uses the robot for precision in joint placement.
- Closing Up: The incision is closed post-procedure.
Risks
- Equipment malfunction
- Learning curve for surgeons
- Potential for longer surgery time initially
Benefits
- Increased accuracy in joint placement
- Smaller incisions
- Potentially reduced recovery time
- Less blood loss during surgery
Joint Replacement Surgery Types
Joint replacement surgery is a widely performed procedure to restore mobility and reduce pain caused by damaged or diseased joints. Below are the main types of joint replacement surgeries:
- Knee Replacement Surgery: Replacing the damaged knee joint with artificial components, as discussed in detail above.
- Hip Replacement Surgery: Involves replacing the hip joint with a prosthesis to treat arthritis, fractures, or other hip-related conditions.
- Shoulder Replacement Surgery: Focuses on replacing the damaged shoulder joint to regain range of motion and alleviate pain.
- Ankle Replacement Surgery: A less common procedure aimed at replacing the ankle joint in cases of severe arthritis or injury.
- Elbow Replacement Surgery: Typically performed to address severe arthritis or trauma, involving the replacement of the elbow joint.
Each type of joint replacement surgery is tailored to the specific needs of the patient, ensuring improved quality of life and functionality. Consulting an expert surgeon like Dr. Madan Mohan Reddy is essential for determining the best treatment option for your condition.
How is a Total Knee Replacement Performed?
A total knee replacement involves:
- Removing damaged cartilage and bone
- Resurfacing the joint with metal and plastic implants
- Restoring alignment and movement
- Techniques like Minimally Invasive Total Knee Replacement reduce tissue trauma
With advancements in the types of knee replacement surgery, and increasing awareness of different knee surgeries, patients are recovering faster. Whether it’s traditional or Minimally Invasive Total Knee Replacement, choosing the right joint replacement surgery types ensures better long-term results.
The right surgeon will guide you through allExploring the Procedure of Knee Replacement Surgery and help determine the best option for your unique needs.
Who Can Benefit from a Knee Replacement?
Before delving into the types of knee replacement surgery, it’s important to understand who is a candidate for this life-changing procedure. Individuals suffering from the following conditions typically benefit from knee replacement surgery:
- Osteoarthritis: The most common form of arthritis that causes the cartilage in the knee joint to break down, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune condition that can lead to inflammation in the joints, including the knees.
- Knee deformities or injuries: Those who have sustained significant knee injuries or fractures may be candidates for joint replacement.
- Chronic knee pain: For individuals whose knee pain has become unmanageable with medications, physical therapy, or other treatments.
Risks of Knee Replacement Surgery
Before choosing the best type of total knee replacement, understanding the risks is crucial.
- Infection – Rare but possible; may require antibiotics or further surgery.
- Blood Clots – Can be prevented with medication and movement post-surgery.
- Implant Wear & Loosening – May require revision surgery in the future.
- Stiffness & Limited Motion – Can be minimized with physical therapy.
- Allergic Reactions to Implants – A rare but potential complication.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of knee replacement surgery is essential for anyone considering treatment for knee pain. With options ranging from total and partial knee replacements to revision surgeries, bilateral procedures, and advanced robotic-assisted techniques, patients have various choices to address their specific needs. Consulting with experts like Dr. Madan Mohan Reddy can provide valuable insights into the best path for your recovery. By educating yourself about different knee surgeries, you can make informed decisions that lead to a better quality of life and improved mobility.