Soft tissue injuries are common occurrences that affect muscles, tendons, ligaments, and other soft tissues in the body. These injuries can happen in many situations, from sports activities to accidents, and can vary in severity. Whether it’s a mild strain or a more severe tear, understanding soft tissue injuries is crucial for effective treatment and recovery. In this blog post, we’ll explore the different types of tissue injuries, their symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and most importantly, how to prevent and treat them.
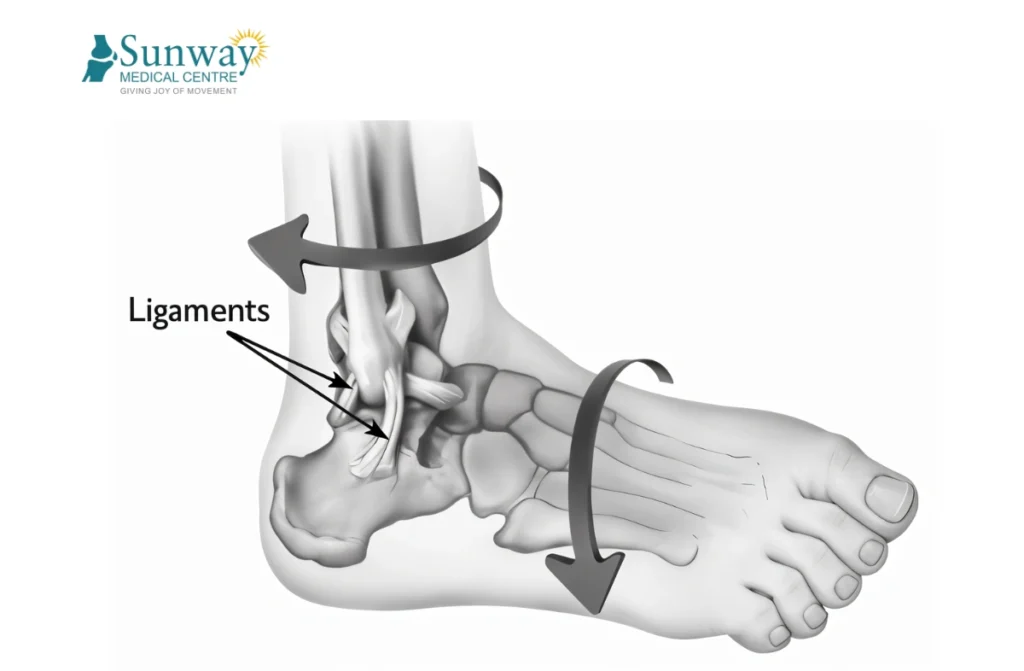
What are Soft Tissue Injuries?
Soft tissue injuries involve damage to the body’s non-bony structures such as muscles, tendons, ligaments, and connective tissues. These injuries typically occur when these tissues are overstretched, torn, or bruised, often due to sudden trauma, repetitive strain, or incorrect body movements during physical activities. From mild sprains and strains to more serious conditions like a soft tissue knee injury, the severity can vary widely. Many people often ask, what is the best treatment for a soft tissue injury? The answer depends on the type and extent of the damage, but early rest, ice application, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E.) are effective first-line measures, while more severe injuries may require physiotherapy or orthopedic care.
Types of Soft Tissue Injuries
- Sprains: Sprains occur when a ligament is stretched or torn, often happening in the knee, ankle, or wrist. This injury is usually caused by a sudden twist or fall.
- Strains: A strain happens when a muscle or tendon is overstretched or torn. This type of injury often affects the rid of back pain, hamstrings, or quadriceps.
- contusion (Bruises): contusion is an injury caused by a direct impact to soft tissue, resulting in bleeding beneath the skin and the formation of a bruise.
- Tendinitis: Tendinitis refers to inflammation of the tendon, often due to overuse, and commonly affects areas like the elbow, shoulder, or knee.
Symptoms
- Pain: Pain is often the first symptom of a soft tissue knee injury treatment, and it can vary in intensity depending on the injury’s severity.
- Swelling: Swelling occurs when blood and fluid accumulate in the injured area as a result of inflammation.
- Bruising: Discoloration of the skin around the injury site often accompanies contusions and is caused by broken blood vessels.
- Limited Range of Motion: The affected area may become stiff, making it difficult to move or use the injured part of the body.
Causes
- Trauma: A sudden impact or forceful movement, such as falling, twisting, or a direct blow.
- Overuse: Repetitive motions or overexertion of muscles and tendons can lead to soft tissue damage, especially in athletes or individuals who perform physical labor.
- Improper Technique: Using improper form or posture during exercise, sports Injuries, or daily activities can strain muscles and ligaments, resulting in injury.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will assess the injury by checking for signs of swelling, bruising, and limited range of motion.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds may be used to assess the extent of soft tissue damage and rule out fractures or other underlying conditions.
- Clinical History: Understanding the circumstances surrounding the injury can help diagnose the type and severity of the soft tissue injury.
Treatment
- Rest and Ice: Resting the injured area and applying ice can help reduce swelling and pain. Ice should be applied in intervals of 15–20 minutes to avoid skin damage.
- Compression and Elevation: Wrapping the injured area with an elastic bandage and elevating it above the heart level can help reduce swelling.
- Pain Relief: Non-prescription options like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used to ease discomfort and reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: After the initial healing phase, physical therapy exercises may be recommended to restore strength and flexibility to the injured area.
How Serious can Soft Tissue Injuries be?
Soft tissue injuries refer to damage involving the muscles, tendons, and ligaments. These tissues support and protect our joints especially the knees, which take on a lot of wear and tear over the years. Common types of injury include sprains (stretched or torn ligaments), strains (injured muscles or tendons), and contusions (bruises).
At first, the pain or swelling may seem manageable. But without proper rest and treatment, these injuries can worsen over time. In particular, a knee soft tissue injury might start as a minor ache and gradually lead to joint stiffness or difficulty walking.For older adults, even a simple soft tissue damage can make everyday tasks like standing up from a chair or climbing stairs more difficult. This can lead to reduced activity levels, increased risk of falls, and a general decline in mobility and independence.
Prevention
- Warm-Up and Stretching: Properly warming up before physical activity and stretching the muscles can help reduce the risk of injury.
- Proper Technique: Learning and using the correct technique during exercises, sports, and daily tasks can prevent strain on soft tissues.
- Rest and Recovery: Taking breaks during physical activity and allowing sufficient recovery time can prevent overuse injuries.
- Strengthening Exercises: Regular strength training exercises can improve muscle and tendon resilience, reducing the risk of soft tissue injuries.
What are the Possible Complications of Soft Tissue Injuries?
When left untreated, soft tissue injuries may not heal correctly and that can cause more trouble down the line. Some of the most common complications include:
- Chronic Pain: Ongoing discomfort in the affected area is one of the first signs that healing isn’t going as it should. Scar tissue can form, and inflammation may continue to flare up over time.
- Joint Instability: Ligament injuries, especially in the knees, can weaken the joint. This makes it easier to re-injure the area and harder to trust your balance, especially when walking or standing for long periods.
- Reduced Mobility: If a soft tissue knee injury heals poorly, you may find your range of motion limited. This can affect how comfortably you move throughout the day and may interfere with your ability to stay active.
- Early Arthritis: Long-term soft tissue damage can place added stress on the bones and cartilage, speeding up the onset of arthritis in the joint. For the knees, this is a major concern especially for older adults already managing age-related joint wear.
Conclusion
In conclusion, soft tissue injuries are a common occurrence in daily life and physical activities. Whether it’s a knee soft tissue injury, muscle strain, or tendon damage, understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for a quick recovery. With proper care, most soft tissue injuries can heal over time, allowing individuals to return to their regular activities. Always remember that prevention is key, and taking steps to protect your body during physical activity can help reduce the likelihood of these injuries.