Understanding the difference between osteoarthritis and osteoporosis is essential for anyone looking to maintain their health as they age. Both conditions are prevalent, especially among older adults, but they affect the body in distinctly different ways. While osteoporosis weakens bones, making them more prone to fractures, osteoarthritis primarily impacts joints, leading to pain and reduced mobility. This blog will explore these conditions in depth, helping you recognize their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Overview
Before diving deeper, it’s important to understand the basic definitions. What is the difference between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis? Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased fracture risk. On the other hand, osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects cartilage, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation. Knowing the difference between osteoarthritis and osteoporosis can help you manage these conditions more effectively.
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis means “porous bones.” It occurs when the body loses too much bone or makes too little bone, leading to weak bones that can break easily. This condition often goes unnoticed until a fracture occurs. Common areas affected include the hip, spine, and wrist.
Symptoms of Osteoporosis
The symptoms of osteoporosis may not appear until a fracture occurs. However, some signs include:
- Fractures: Occurring more easily than expected, often from minor falls or injuries.
- Loss of height: Gradual height loss can indicate bone weakening, sometimes leading to a stooped posture.
- Stooped posture: A bent forward position may develop over time, known as kyphosis.
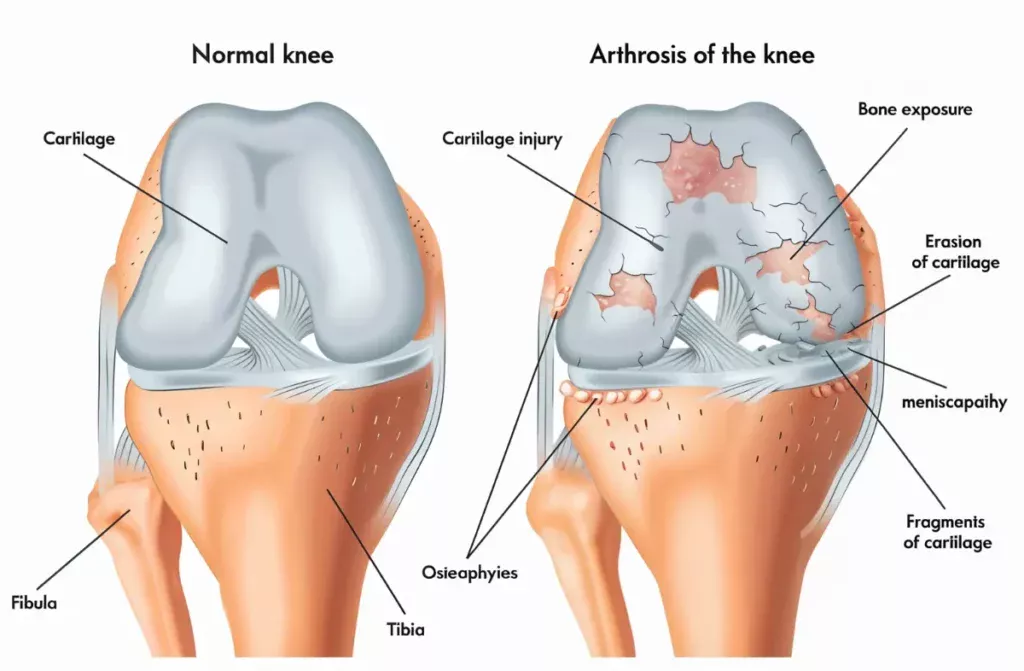
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis, often referred to as “wear and tear” arthritis, occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones wears down over time. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected joints, making daily activities challenging. It’s most commonly found in knees, hips, and hands.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
The symptoms of osteoarthritis can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Joint Pain: Aching or soreness in the affected joints, especially after movement.
- Stiffness: Particularly noticeable in the morning or after sitting for a long time.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the joints can cause swelling and tenderness.
Causes
Both osteoporosis and osteoarthritis are influenced by a mix of genetic and environmental factors. Osteoporosis can result from hormonal changes, especially post-menopause in women. Osteoarthritis can develop from joint injuries, obesity, or age-related wear and tear. Understanding these factors is key to knowing what is the difference between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis and how to manage them.
Osteoporosis Risk Factors and Diagnosis
Several risk factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis, including:
- Age: The risk increases as you get older.
- Gender: Women are at higher risk, especially after menopause.
- Family History: Genetics play a role in bone density.
If you’ve ever wondered, “Is osteoporosis the same as osteoarthritis?” the answer is no. These are two entirely different conditions that affect the body in unique ways.
Osteoarthritis Risk Factors and Diagnosis
Osteoarthritis can be diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluations and imaging tests. Risk factors include:
- Age: The likelihood increases with age.
- Obesity: Extra body weight puts more stress on the joints.
- Injuries: Past joint injuries can increase the risk of osteoarthritis later in life.
Understanding what’s the difference between osteoporosis and arthritis can guide you toward the right preventive and treatment measures.
Osteoarthritis vs. Osteoporosis: How Are They Different?
Understanding the difference between osteoarthritis and osteoporosis lies in their impact on the body: osteoporosis affects bone density and strength, whereas osteoarthritis impacts joint cartilage. For those wondering, is osteoporosis the same as osteoarthritis, the answer is a clear no. Additionally, many people confuse the difference between osteoarthritis and arthritis, but arthritis is a broader term encompassing various joint conditions, including osteoarthritis.
What’s the difference between osteoporosis and arthritis?
Osteoporosis is a bone disease, while arthritis refers to various joint diseases, including osteoarthritis, which specifically damages joint cartilage.
By understanding these distinctions, you can better manage your health and take appropriate preventative measures. Recognizing the difference between osteoarthritis and osteoporosis ensures timely interventions and improved quality of life.
Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis
Treatment for osteoarthritis focuses on relieving symptoms and improving joint function. Options include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises can strengthen the muscles around the joint, improving stability and function.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on weight-bearing joints, helping alleviate symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement may be necessary to restore mobility and reduce pain.
By understanding the difference between osteoarthritis and arthritis, you can take proactive steps to manage these conditions effectively and improve your quality of life.
Prevention
Preventing both osteoporosis and osteoarthritis involves several lifestyle choices:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health. Foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and fish are excellent sources.
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, particularly weight-bearing and strength-training exercises, can strengthen bones and improve joint flexibility.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine visits to your healthcare provider can catch issues early and allow for proactive management.
Risk factors for Osteoarthritis vs. Osteoporosis? Are They Inherited?
Risk factors for both conditions can include age, weight, and family history. Osteoporosis risk is often linked to genetics, with a family history of fractures or low bone density increasing the likelihood of developing the disease. Osteoarthritis can also stem from previous injuries, obesity, and repetitive stress on joints.
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures. For example, if there is a family history of osteoporosis, a person might focus on dietary changes and regular exercise early in life to strengthen their bones.
Ways to Improve Your Bone and Joint Health
To maintain bone and joint health, consider these practical tips:
- Nutrition: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Calcium and vitamin D are crucial for bone health.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling. Incorporating strength training can also help.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can weaken bones and joints, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis.
- Limit Alcohol: Excessive alcohol intake can interfere with bone health and increase the risk of falls.
Which is more painful, Osteoarthritis or Osteoporosis?
While both conditions can be painful, osteoarthritis typically causes more noticeable discomfort due to joint inflammation and stiffness. Individuals with osteoarthritis often experience daily pain that can significantly affect their quality of life. In contrast, osteoporosis may lead to severe pain after a fracture occurs, but the condition itself often remains silent until a break happens.
When it comes to lifestyle impacts, osteoarthritis can be more debilitating, as it directly affects mobility and everyday activities. Individuals with osteoarthritis may struggle with tasks like climbing stairs or even walking, which can lead to a more significant reduction in quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between osteoarthritis and osteoporosis is vital for effective management and prevention. While osteoporosis leads to weakened bones and increased fracture risk, osteoarthritis affects joints, causing pain and stiffness. Recognizing the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options for both conditions can empower you to make informed health decisions. If you suspect you have either condition, consult your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and care. Early detection and intervention can make a significant difference in managing these conditions effectively.
Read also Factors that Affect Bone Healing.